
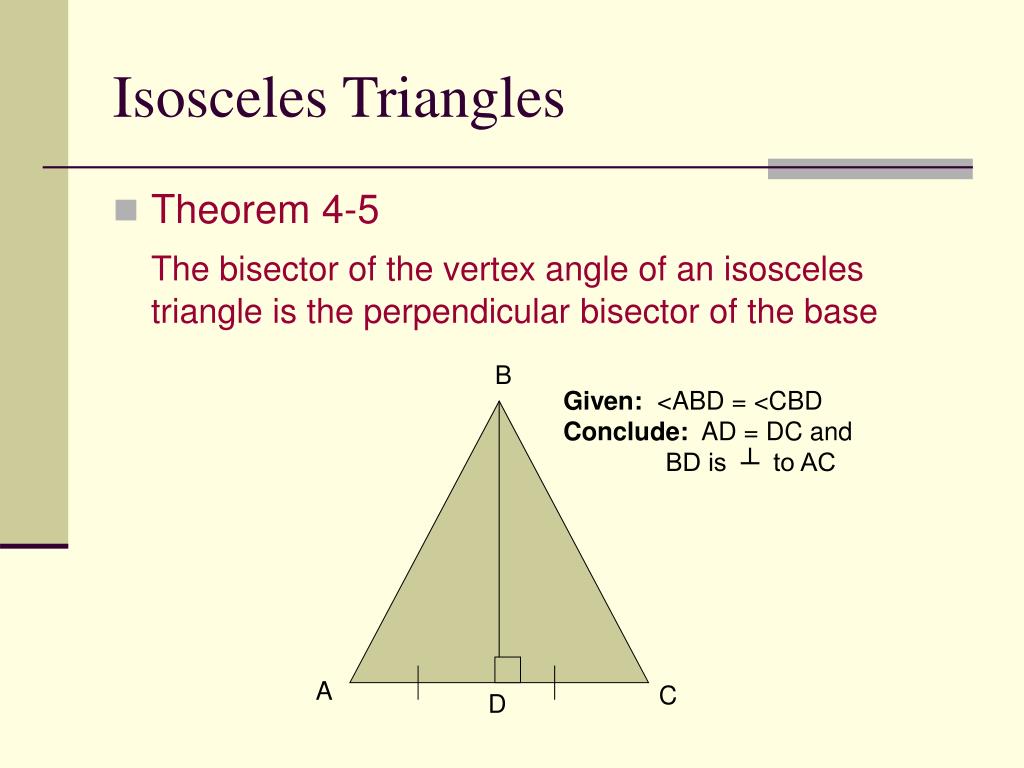
What is the Converse of Isosceles Triangle Theorem? The two triangles now formed with altitude as its common side can be proved congruent by SSS congruence followed by proving the angles opposite to the equal sides to be equal by CPCT. An isosceles triangle can be drawn, followed by constructing its altitude. Isosceles triangle theorem can be proved by using the congruence properties and properties of an isosceles triangle. Isosceles triangle theorem states that, if two sides of an isosceles triangle are equal then the angles opposite to the equal sides will also have the same measure. Related ArticlesĬheck these articles related to the concept of the isosceles triangle theorem.įAQs on Isosceles Triangle Theorem What is Isosceles Triangle Theorem? Hence we have proved that, if two angles of a triangle are congruent, then the sides opposite to the congruent angles are equal. Proof: We know that the altitude of a triangle is always at a right angle with the side on which it is dropped. Let's draw a triangle with two congruent angles as shown in the figure below with the markings as indicated.

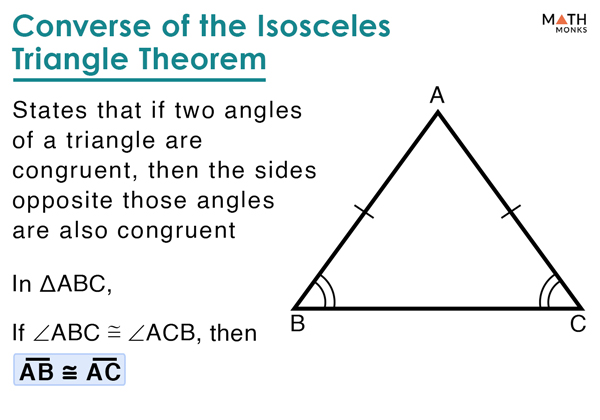
Converse of Isosceles Triangle Theorem Proof We will be using the properties of the isosceles triangle to prove the converse as discussed below. This is exactly the reverse of the theorem we discussed above. The converse of isosceles triangle theorem states that if two angles of a triangle are congruent, then the sides opposite to the congruent angles are equal. Hence, we have proved that if two sides of a triangle are congruent, then the angles opposite to the congruent sides are equal. Proof: We know, that the altitude of an isosceles triangle from the vertex is the perpendicular bisector of the third side. Given: ∆ABC is an isosceles triangle with AB = AC.Ĭonstruction: Altitude AD from vertex A to the side BC. Let's draw an isosceles triangle with two equal sides as shown in the figure below. To understand the isosceles triangle theorem, we will be using the properties of an isosceles triangle for the proof as discussed below. The angle bisector of the triangle is perpendicular to the side with different length.Isosceles triangle theorem states that if two sides of a triangle are congruent, then the angles opposite to the congruent sides are also congruent. The angle bisector divides the unequal angle into equal half. Note: In isosceles triangle the two sides are equal and the two angles corresponding to the sides are equal. $\therefore $ proved the converse Isosceles Triangle Theorem. Since corresponding part of congruent triangles are congruent, so the two sides of the triangle will be equal, which is So by the$AAS$ property of triangle the two triangle $\vartriangle ABD$ and $\vartriangle ACD$ are congruent. In both the triangles $\vartriangle ABD$ and $\vartriangle ACD$ the line segment $AD$ which is also the angle bisector of $\angle A$ is common.
These two angles are equal because the line $AD$ which was constructed is a bisector of the angle $\angle BAC$.
These angles are equal as stated in the theorem.

The three properties which make the triangle $\vartriangle ABD$ and $\vartriangle ACD$ congruent are Now, on analysing the above triangle we see that the triangle could be proved congruent.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
